Are you looking for the standard definition of project management terms? If so, you’re on the right page. There are several of these terminologies that can even get a pro scrambling the web.
And that’s why this post compiles all the basic project management terms. Yes, this is the ultimate project management glossary.
Project Management Terms and Definitions
A
Acceptance criteria
These are the conditions and requirements that need to be met before a deliverable can be accepted by a client.
Acceptance test
A testing process to ensure that the deliverable works in the proper way. Through this process, users can identify any potential problems the product may have.
Action plan
An action plan in project management is a detailed strategy that lists all the steps to complete a project. It contains the tasks, timeline, and resources involved in the project.
Activity
It refers to a phase of the project plan. It is a unit of work that members need to complete before the project can proceed to its next phase.
Activities are assigned to individual team members to complete a specific goal within the project.
AOA – Activity on Arrow diagram
It is a network diagram technique where arrows represent activities. It is used for mapping and scheduling activities.
AON – Activity on Node diagram
Similar to the above, with the difference of nodes representing activities. Here, arrows show relationships between activities.
ACWP – Actual Cost of Work Performed
It refers to the actual cost sustained for a work that’s done.
APF – Adaptive Project Framework
APF is a project management approach where the project is reviewed at each stage. It allows you to revise and improve project decisions after considering the effect of your decisions in the previous stages of the project.
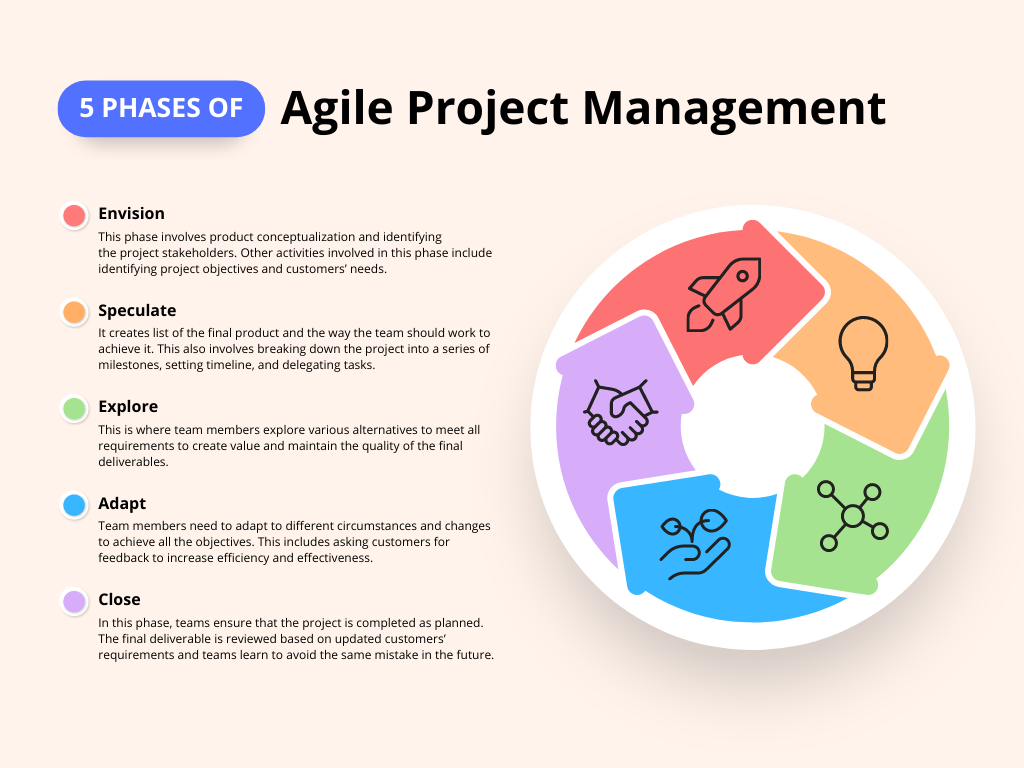
Agile methodology
Agile is a flexible project management methodology that allows for frequent revisions. It focuses on collaboration, customer satisfaction, and adaptability.
Allocation
Refers to the act of distributing resources for work on hand.
Alternative analysis
The evaluation of different routes you can take to meet a project’s goal.
Assumptions
Assumptions mean considering factors relating to a project to be true without having any substantial proof.
B
Balancing
An act that involves making changes to maintain the project’s balance and keeping it on track toward the project’s objectives.
Bar chart
A chart that represents the project’s schedule of activities in a logical order of the start and end dates.
Baseline
The approved schedule and cost that you set for your project at the starting point.
Benefits
The measurable improvement a stakeholder or client experiences from the results of a project.
Brief
A document that outlines the elements of a project.
Budget
The total amount of money allocated to a project after considering the project’s requirements, tasks, milestones, and goals.
BCWP – Budgeted Cost of Work Performed
It refers to the budget allocated to work done. It shows how much money was spent and on which task.
BCWS – Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled
Refers to the budget allocated to work which is planned to be completed in a period. It shows how much money should have been spent and on which task.
Burn down chart
A burn-down chart shows the work remaining and the time remaining to complete that work.
Business value
Refers to a total of positive effects a project has on the business.
C
Calendar
It shows the days and times at which a team should work on a project.
CMM – Capability Mature Model
A method used to refine and develop the software processes of an organization.
Case study
A case study refers to intensive research on the working of a company or industry.
CAPM – Certified Associate in Project Management
CAPM is a certification provided by the PMI (Project Management Institute). A holder of this certificate is understood to be aware of the necessary terminologies and knowledge of the field.
Change control
Change control refers to the process of managing any changes to a project.
Change management
A method of managing the change control process that’s defined above. It involves planning, executing, and monitoring changes to ensure that they are not only well-executed but also have the desired effect on the project or business.
Client
Refers to the person or group who requires the project. Every action the project team takes is to meet the client’s requirements and expectations.
Closing phase
The last stage of the project management life cycle, when all tasks have been completed and are ready to be handed over to the client.
Communication management
A series of tasks aimed at ensuring there is a proper flow of communication within the project team, clients, and stakeholders. It involves tracking whether messages were received by the right people.
Constraint
It simply refers to the limitations of a project.
Cost
The total sum of money needed to complete a project.
Cost overrun
It is a situation whereby the actual cost spent on a project exceeds the planned amount.
Control
The fourth phase of the project life cycle. Project control is all about keeping the project on track through supervision on the part of the project manager.
D
Dashboard
The dashboard is a visual representation showing a collection of key data and metrics about a project.
Decomposition
Decomposition in project management is the breaking down of a large and complex project into smaller and more manageable tasks.
Deliverable
The end product of a project that is presented to clients.
Dependency
This is a term used to describe interrelated project tasks. This means for a task to be completed, another task must first be completed.
Duration
The amount of time it takes to complete an activity, task, or project.
E
Effort
Amount of work required for completing a task.
Estimation
The process of predicting the time, resources, and cost needed to complete a task by analyzing currently available data.
Event Chain Diagram
A diagram showing the order of events in a project and how they affect one another.
Execution phase
The third phase of the project life cycle. It is when the project team actually carries out the task.
XPM – Extreme Project Management
A method of project management that you implement when facing complex and uncertain projects.
F
Fishbone diagram
A diagram aimed at identifying the potential causes of an issue.
Fixed duration
Refers to a task that has a fixed time for completion.
Float
The amount of time a task can be delayed without affecting other tasks or the project itself.
G
Gantt Chart
A graphical representation of tasks involved in a project against time.
Goals
The project or business objectives.
H
Handover
A point where you give the project deliverables to the client.
Historical information
Refers to the act of using past project data to plan future projects.
Human resource management
The management of employees and team members to carry out a project.
Hybrid Methodology
Refers to a mix of two distinct methodologies (usually waterfall and agile) to manage a project.
I
Initiation
The first phase of the project life cycle. Here, the project’s scope and goals are defined.
Issue
Refers to any factor that can raise challenges for the project.
Iterative development
Refers to the practice of improving and refining a project.
K
Kanban Methodology
A project management method that focuses on reducing waste and inefficiency.
KPI – Key Performance Indicator
Refers to metrics used in measuring a project’s success.
Kickoff meeting
As the name implies, this refers to the meeting held by stakeholders to start a project.
L
Life cycle
The sequence of tasks that needs completion for a project’s success.
Linear scheduling method
A scheduling method for allocating resources when there are repetitive tasks in a project.
M
Management process
The process of planning and monitoring a project to meet a set goal or objective.
Milestone
A point of progress within the project life cycle.
Motivation
Refers to the act of stimulating individuals towards achieving the project’s goal.
N
Negotiation
A discussion between parties for resolving an issue or arriving at an agreement.
Network Path
In project management, this refers to a continuous series of logically connected tasks.
O
Objectives
What you want to achieve at the end of a project.
Output
Output refers to the end product or result of a project.
P
Phase
Phase refers to a grouping or collection of activities within a project.
Planning
It involves creating a course of action to meet the project’s goals and objectives. It’s the second stage in the life cycle of a project.
PRINCE2 – Projects in a Controlled Environment
An approach to project management that emphasizes organization and control. It is also a project certification that’s mostly popular in the UK and Europe.
PRiSM – Projects Integrating Sustainable Methods
PRiSM is a methodology aiming to complete projects and reduce negative impacts on the society.
PBS – Product Breakdown Structure
A hierarchal structure showing the outcomes a project aims to deliver.
Program
Program in project management refers to a collective group of projects managed together as one full large project.
Program management
Program management is the process of managing a program to improve business performance in the long term.
PCM – Project Cost Management
It simply refers to the management of costs throughout the project’s life cycle.
PMBOK – Project Management Body of Knowledge
PMBOK is cumulative of standard terminologies, guidelines, and best practices about project management.
PMP – Project Management Professional
A certificate offered by the Project Management Institute. It is a highly recognized certificate in the industry.
Project Manager
A person who manages a project.
Project team
A team of those working together to complete a project and meet its goals.
Q
Quality
The degree to which a product/deliverable and its characteristics satisfies the expectations of clients and stakeholders.
Quality control
The process of ensuring that a product’s quality satisfies the clients.
Quality planning
A process that involves the identification of the expected quality of a product and taking action to ensure that the expectations are met. It also involves taking corrective measures if the quality doesn’t meet the standard.
Note that quality planning occurs before the execution of a project while quality control may occur anytime during or even after the project.
R
RAID log
RAID stands for Risks, Assumptions, Issues, and Dependencies. RAID logs are sheets that you use to manage and track these four key aspects of a project.
RASCI chart
RASCI stands for Responsible, Accountable, Supporting Consulted, and Informed.
Used interchangeably with RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed). The chart is a tool used to identify the responsibilities and roles of all stakeholders in the project. This is done at the initiation phase of the project management life cycle.
Reporting
Creating a document that shows the results of the project at a point in the project’s life cycle.
Resources
An asset that’s necessary for a project’s completion.
Resource allocation
The distribution of resources logically and effectively to aid in the project’s completion.
Resource management
A process of planning, monitoring, and distributing resources to complete a project and meet its goals.
Note that resource allocation is just a process in resource management.
Risk
The probability of something happening that may threaten the project’s success.
Risk management
A process that involves the identification of risks and the action taken to manage and minimize them.
S
Schedule
A list providing an overview of the project at hand. It contains the tasks, milestones, start and end dates, resources, and duration of the project.
Schedule baseline
A schedule baseline is the schedule created before the project begins and it’s approved by stakeholders. It is used to assess performance and is rarely modified.
Scope
A part of the planning phase that involves determining specific goals for the project.
Scope baseline
The approved version of the scope that’s defined above. Used to assess project performance.
Scrum methodology
Scrum is a type of agile methodology that works on five major values (commitment, courage, focus, openness, and respect) aimed at satisfying clients with transparency and clarity.
Sponsor
Those at the senior management level that provide support for a project such as resources and funding.
Stakeholder
Refers to a person interested in a project’s outcome. Stakeholders include the project team, sponsors, executives, clients, and end users.
T
Task
A piece of work that needs completion for a project to meet its goals.
Testing
A phase that involves the appraisal of a product to determine if requirements have been met.
Time limit
A duration of time where a project or task must have been completed.
Timeline
A schedule showing all the tasks and activities involved in a project.
Tolerance
Project tolerance is a permissible boundary where you can make changes to a product without needing the approval of stakeholders. Any change that exceeds the tolerance may be rejected.
U
Use case
A scenario where a final user may require the services of a product.
V
Variance analysis
The practice of comparing project results with what was planned.
Virtual team
A project team whereby members operate from several locations and collaborate through electronic means. A virtual team may also include those from different organizations.
W
Waterfall methodology
The waterfall methodology is a linear approach to project management that moves from phase to phase. That is, members are required to complete a phase before moving to the next.
WBS – Work Breakdown Structure
WBS is a structure that divides large projects into a step-by-step format. By doing so, it makes large projects easy to complete.
Workload management
Workload management is a way of planning, monitoring, and allocating workload among team members. Resources are distributed fairly alongside the workload.
Workstream
Series of related tasks or activities that needs completion to meet project goals.
Wrapping Up the Project Management Glossary

Project management is organizing, planning, and managing resources toward achieving a project’s goals. It is a way of ensuring that tasks are effectively executed and on time. The terms above are all areas relating to this broad field of study and profession. You can get some tips and info concerning this field here at Prolific Managers.